The Vera C. Rubin Observatory has launched its first photographs because it begins its 10-year mission conducting the Legacy Survey of Area and Time (LSST).
The LSST will revolutionize astronomy with certainly one of its main goals being the investigation of dark energy, the mysterious pressure driving the accelerating enlargement of the universe, and dark matter, the unusual substance that accounts for 85% of the “stuff” within the cosmos however stays successfully invisible.
From its perch atop Cerro Pachón in Chile, a mountain that rises round 5,200 ft (1,600 meters) above sea stage, Rubin scans your complete night time sky over the Southern Hemisphere as soon as each three nights. This endeavor would be the most in depth steady mapping of the southern sky ever tried, and shall be carried out by Rubin utilizing the 8.4-meter Simonyi Survey Telescope and the LSST camera (LSSTCam), the largest digital camera ever constructed at across the measurement of a small automobile.
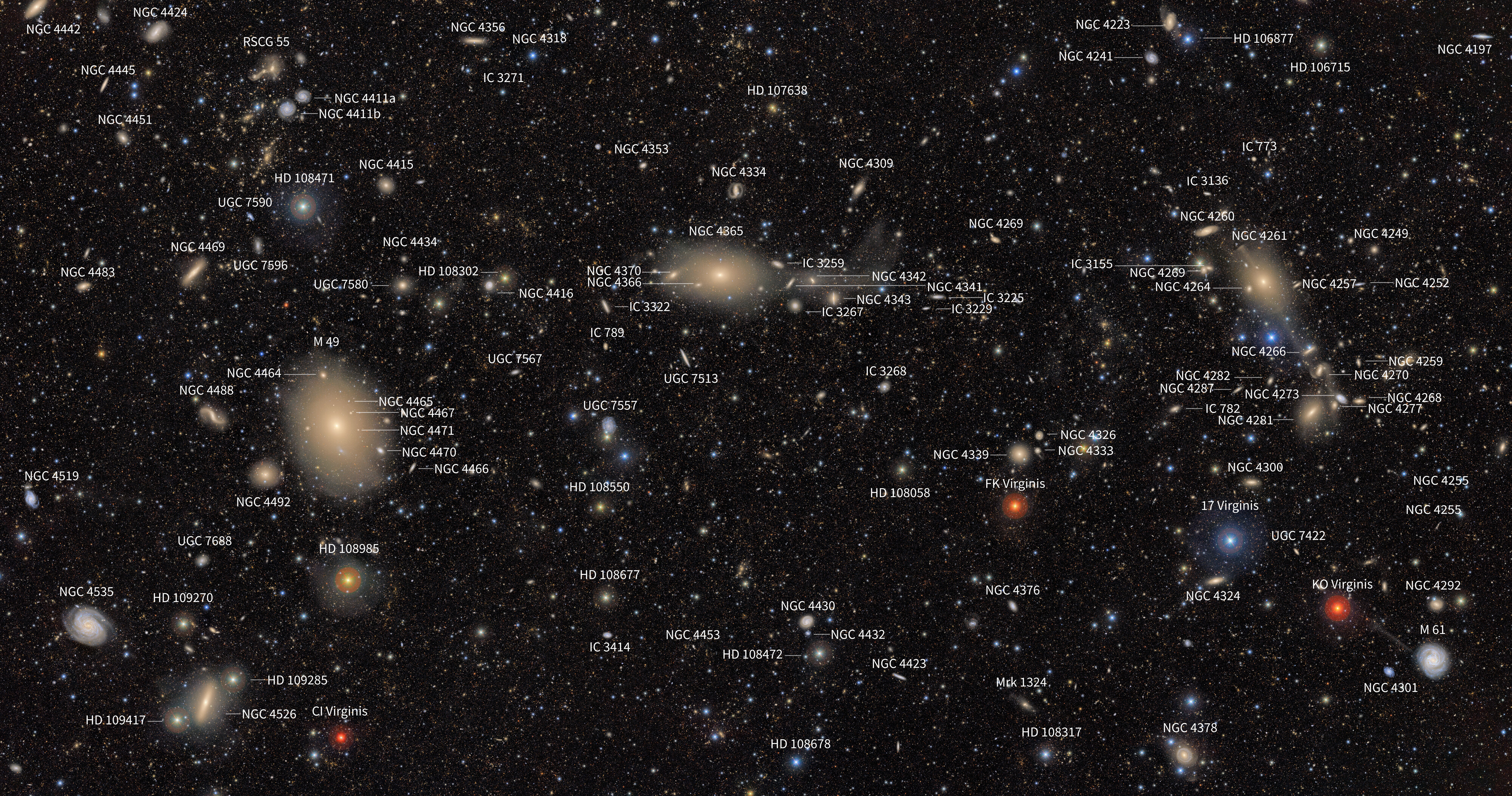
Only one picture from the LSSTCam covers an space equal to the scale of 45 full moons within the sky. Above is the observatory’s first picture of the Virgo cluster, an unlimited cluster of galaxies situated round 53.8 million light-years from Earth. The picture reveals an unlimited array of celestial objects, together with galaxies and stars. Demonstrating the true potential of Rubin, this picture alone comprises a wealthy tapestry of about 10 million galaxies.
Staggeringly, the ten million galaxies within the above picture are simply 0.05% of the variety of round 20 billion galaxies that Rubin may have imaged by the top of the LSST. The truth is, in a decade, Rubin may have collected information on an estimated 40 billion celestial our bodies, that means we may have seen extra heavenly our bodies than there are people alive for the primary time.
Unsurprisingly, many of those objects are utterly new and considered by humanity for the primary time as we speak. The objects which can be acquainted have been highlighted within the picture under.
“The Vera C. Rubin Observatory will permit us so as to add depth and dynamism to the statement of the universe,” Roberto Ragazzoni, president of the Nationwide Institute for Astrophysics (INAF), mentioned in an announcement.
“With this 8-meter class telescope able to repeatedly mapping the southern sky each three days, we enter the period of ‘astro-cinematography’, exploring a brand new dimension: that of time, with which we count on to check the cosmos with a brand new perspective, which is now attainable thanks additionally to using new data applied sciences to course of a mass of knowledge that might in any other case be inscrutable.”
If it strikes, Rubin will see it
One of the vital spectacular skills of Rubin shall be its functionality to check objects that change in brightness over time because it builds the “biggest film of all time.” This distinctive energy comes from the truth that Rubin can scan the sky at superfast speeds, round 10 to 100 instances quicker than comparable massive telescopes.
The “transients” it sees will embrace over 100 million variable stars altering their brightness due to pulsations, thermal instabilities, and even due to planets “transiting,” or passing between Rubin and their seen disks.
Rubin will even have the ability to observe thousands and thousands of huge stars as they finish their lives and bear supernova explosions. The groundbreaking observatory will even examine so-called “sort Ia supernovas,” triggered when useless star-white dwarfs bear runaway nuclear explosions after overfeeding on stellar companions.
Type Ia supernovas are often known as “customary candles” on account of the truth that their constant luminosities permit astronomers to make use of them to measure cosmic distances. Thus, Rubin will even make an oblique influence on astronomy by offering scientists with a wealth of recent and better-understood distances between objects within the universe.
Nearer to residence, by observing objects as they modify in brightness within the night-sky, Rubin will present astronomers with a greater image of asteroids and small our bodies as they orbit Earth. This might assist house businesses like NASA assess potential threats to Earth and defend in opposition to asteroids.
The YouTube video under reveals over 2,100 new asteroids found by Rubin in its first week of operations alone.
“If one thing within the sky strikes or modifications, Rubin will detect it and distribute the knowledge in actual time to your complete world. Which means we can observe transient phenomena in motion, making new, typically sudden, astrophysical discoveries attainable,” mentioned Sara (Rosaria) Bonito of the Board of Administrators of the LSST Discovery Alliance of the Vera C. Rubin Observatory.
“Rubin will produce a real multi-colored film of the sky, lasting a whole decade. A film that can permit us to see the universe as by no means earlier than: not simply via static photographs, however in dynamic evolution.”
Rubin’s energy lies within the particulars
Hours earlier than the discharge of the primary photographs above at 11 a.m. EDT (1500 GMT) on Monday (June 23), the Rubin crew launched a number of smaller “preview” photographs which can be smaller sections of those bigger photographs. These give most of the people a chance to witness the unimaginable element in photographs captured by the LSST digital camera.
“These sneak preview photographs already spotlight the distinctiveness of Rubin to take a look at the cosmos in a method that now we have by no means carried out earlier than, bringing the sky to life!” Andrés Alejandro Plazas Malagón, a researcher at Stanford College and a part of the Rubin Observatory’s Group Science Crew, instructed Area.com. “These preview photographs additionally already spotlight the sophistication and energy of the software program used to cut back or ‘clear’ the pictures: the LSST Science Pipelines.”
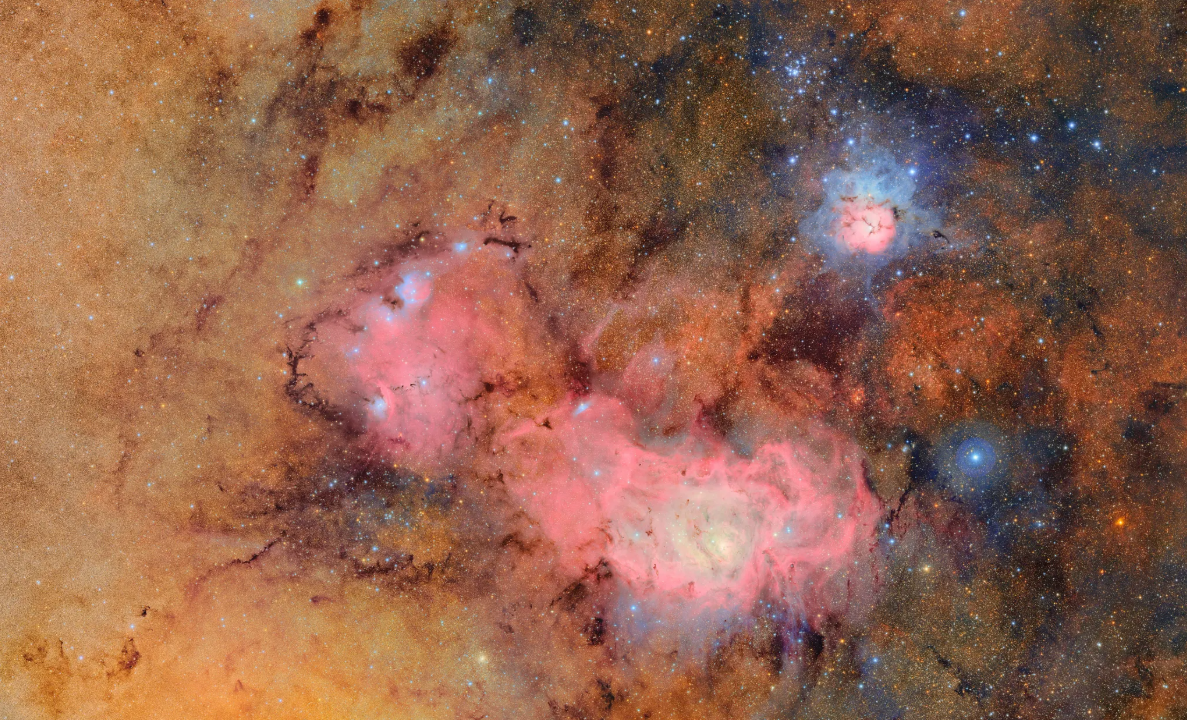
The picture under reveals the Triffid nebula (often known as Messier 20 or NGC 6514) within the prime proper, which is situated round 9,000 light-years from Earth, and the Lagoon nebula (Messier 8 or NGC 6523), estimated to be 4,000 to six,000 light-years away. These are areas during which clouds of fuel and dirt are condensing to delivery new stars.
The above image combines 678 separate photographs taken by Rubin over simply over 7 hours of observing time. By combining photographs like this, Rubin is able to revealing particulars in any other case too faint to see or virtually invisible. This reveals the clouds of fuel and dirt that comprise these nebulae in unimaginable element.
“The Trifod-Lagoon picture reveals these two nebulae or ‘stellar nurseries’ highlighting areas of fuel and dirt, constituted of about 678 particular person photographs,” Plazas Malagón mentioned. “It is spectacular how the massive discipline of view of LSSTCam captured the scene all of sudden!”
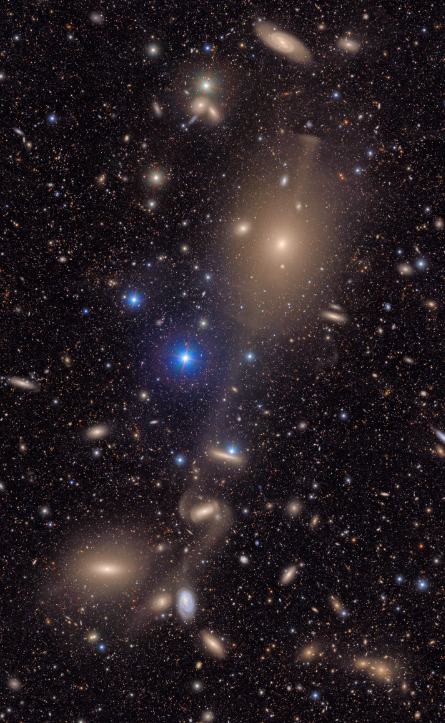
The picture under reveals a small part of Rubin’s complete view of the Virgo cluster. The intense foreground stars on this picture are situated nearer to residence, mendacity within the Milky Method. Within the background are many galaxies much more distant than the Virgo cluster.
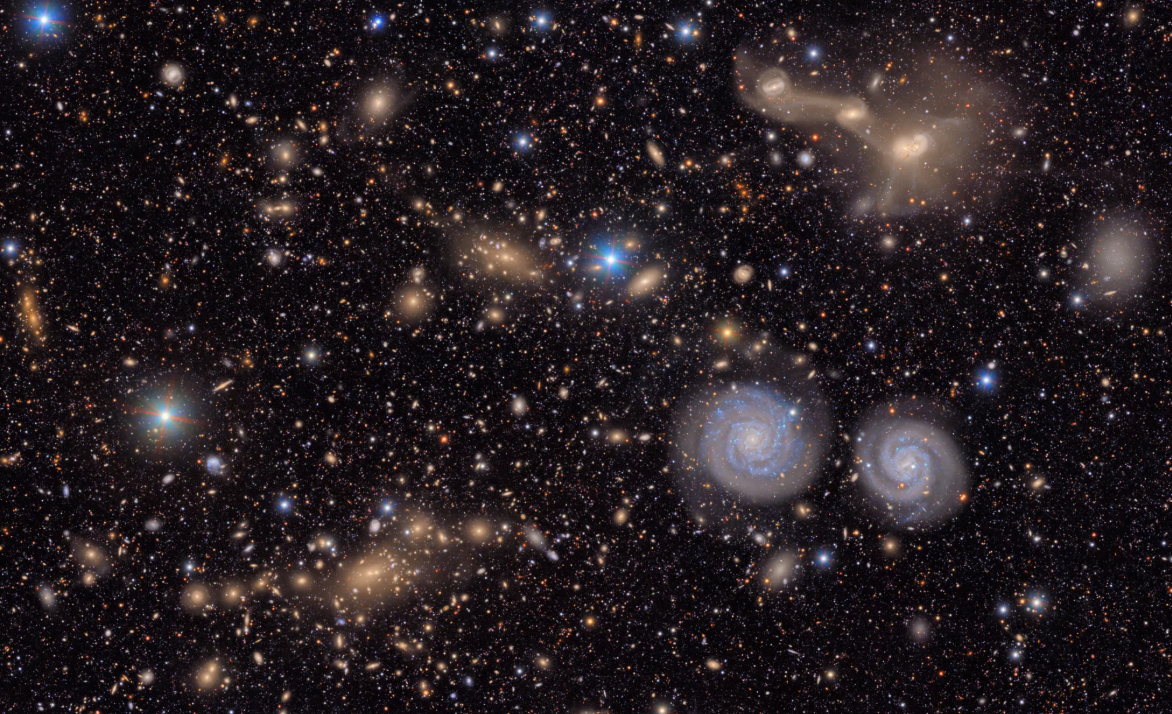
The picture under reveals one other small slice of Rubin’s complete view of the Virgo cluster. Seen within the decrease proper of the picture are two distinguished spiral galaxies. Within the higher proper of the picture are three galaxies which can be colliding and merging.
The picture additionally comprises a number of different teams of distant galaxies, in addition to a wealth of stars in our galaxy. It is only one fiftieth of your complete picture it got here from.
“The opposite preview photographs present a fraction of the Virgo cluster, a galaxy cluster of about 1,000 galaxies. Constructed from about 10 hours of knowledge, we already see the aptitude of Rubin to seize the faintest objects with beautiful element, which is able to allow wonderful science. And these photographs are nearly 2 % of the sphere of view of a single LSSTcam picture!” Plazas Malagón mentioned.
Following the discharge of those photographs, the subsequent massive step for Rubin with be the start of the LSST, which ought to happen over the subsequent few months.
“The Vera C. Rubin Observatory and its first LSST venture are a novel alternative for the brand new technology,” Bonito mentioned. “It’s a nice legacy for anybody who needs to method scientific disciplines, providing a revolutionary instrument for astrophysics and new applied sciences for information interpretation.”
Bonito added that the astrophysics that may be carried out with Rubin is extraordinarily diversified: a single statement marketing campaign will permit us to answer very broad scientific themes, which concern our galaxy but in addition darkish matter, our photo voltaic system, and even essentially the most unpredictable phenomena that happen within the sky.”
And with 10 years of the LSST forward of it, the way forward for Rubin and astronomy generally is brilliant.
“These preview photographs additionally already spotlight the sophistication and energy of the LSST Science Pipelines software program used to cut back or ‘clear’ the pictures,” Plazas Malagón concluded. “As an observational cosmologist and having labored within the improvement of the LSST Science Pipelines and the characterization of the LSSTCam, I am proud and past enthusiastic about what’s coming!”
To dive into the primary picture from Rubin and probe for your self, go to the Vera C. Rubin Observatory SkyViewer page.