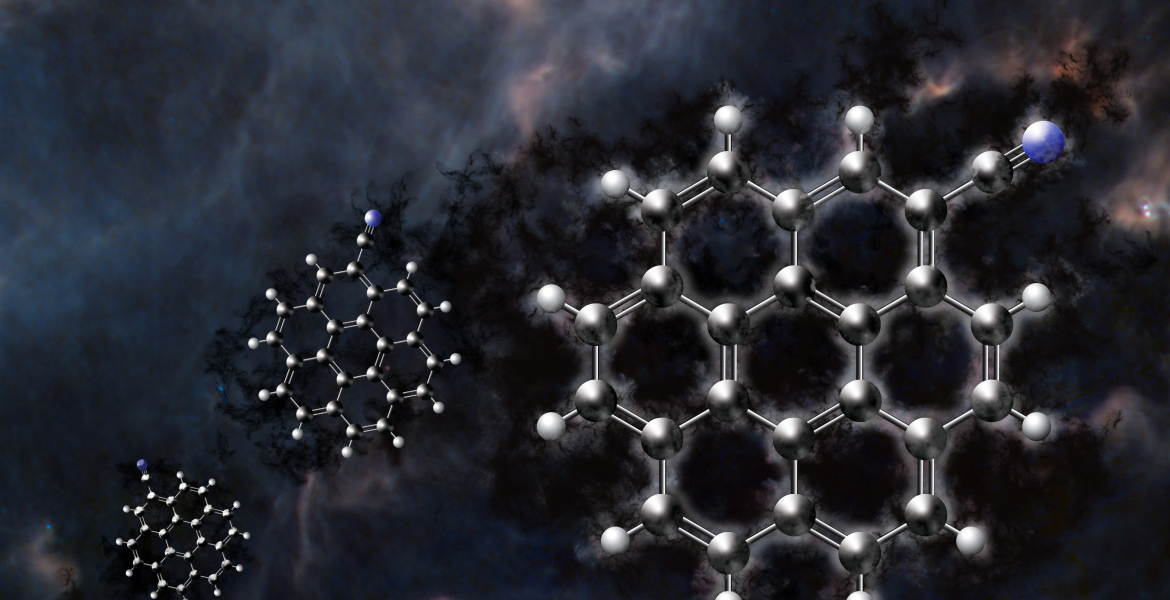
Scientists are claiming a “cosmic chemistry breakthrough” following the invention of a giant “fragrant” molecule in deep area. The invention means that these molecules may assist seed planetary techniques with carbon, supporting the event of molecules wanted for all times.
The molecule, referred to as cyanocoronene, belongs to a category of carbon-based natural compounds referred to as polycyclic fragrant hydrocarbons (PAHs), that are made up of a number of fused fragrant rings — constructions wherein electrons are shared throughout double-bonded carbon atoms, giving them distinctive chemical stability.
“PAHs are thought to lock away a big fraction of the universe’s carbon and play a key function within the chemistry that results in the formation of stars and planets,” Nationwide Radio Astronomy Observatory representatives wrote in a statement. “Till now, solely smaller PAHs had been detected in area, with this new discovery considerably pushing the recognized dimension restrict.”
The scientists decided that cyanocoronene can type effectively within the chilly circumstances of area by means of reactions between coronene and extremely reactive cyanide radicals at low temperatures.
“This implies the chemistry that builds advanced organics can occur even earlier than stars are born,” the researchers wrote, highlighting that such prebiotic molecules could also be frequent components within the early phases of star and planet formation.
The cyanocoronene was recognized by the Green Bank Telescope (GBT), a part of the Nationwide Radio Astronomy Observatory, within the Taurus Molecular Cloud (TMC-1). This star-forming area, situated within the constellations Taurus and Auriga, is thought for its wealthy and sophisticated chemistry.
The GBT — situated in Inexperienced Financial institution, West Virginia — is the world’s largest totally steerable radio telescope. Standing 485 toes (148 meters) tall with a dish 100 meters (330 toes) in diameter, the GBT is a necessary instrument for detecting faint radio indicators from deep area, together with these emitted by molecules like cyanocoronene.
In contrast to optical telescopes, which acquire seen mild, the GBT is designed to detect radio waves, a kind of electromagnetic radiation with for much longer wavelengths. These waves are sometimes emitted by chilly, dense areas of area, just like the TMC-1, the place new stars and sophisticated natural molecules can type.
To establish a particular molecule in area, scientists first measure its microwave spectrum in a laboratory. Every molecule has a novel “fingerprint” — a sample of vitality transitions that seems as traces within the radio spectrum. With this data in hand, scientists use the GBT to gather radio waves and search for a match.
Within the case of cyanocoronene, the researchers discovered a number of matching spectral traces within the GBT’s information, confirming the presence of the molecule in TMC-1 with distinctive confidence far past the statistical likelihood that it will happen randomly.The invention opens the door for astronomers and astrochemists to seek for even bigger PAHs and associated molecules.
Scientists are actually particularly considering how these constructions evolve, fragment or work together with different molecules underneath the affect of ultraviolet mild, cosmic rays and shocks in interstellar space.
“Every new detection brings us nearer to understanding the origins of advanced natural chemistry within the universe — and maybe, the origins of the constructing blocks of life themselves,” Gabi Wenzel, a analysis scientist within the Division of Chemistry at MIT and the Harvard and Smithsonian Heart for Astrophysics and lead writer of the analysis, mentioned within the assertion.
The analysis was introduced earlier this month on the 246th assembly of the American Astronomical Society in Anchorage, Alaska.