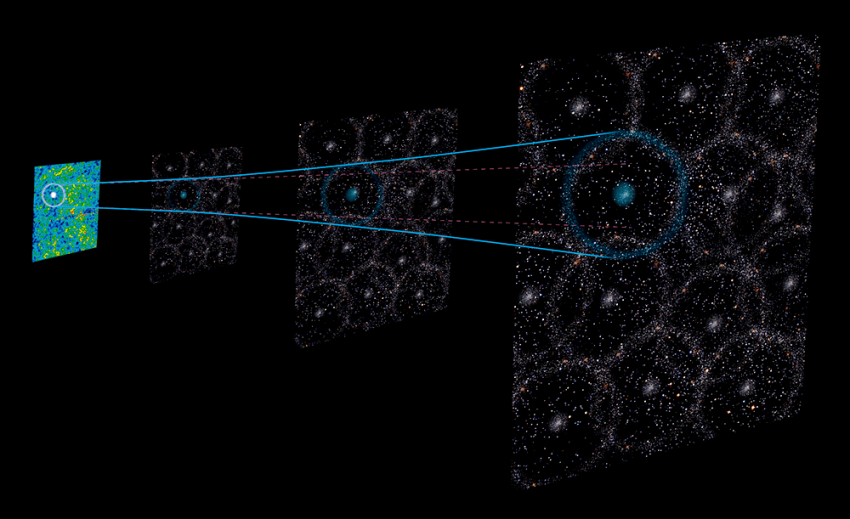
Earth, its cosmic dwelling the Milky Manner, and even the very native area of universe round us could possibly be located inside a void of low density in comparison with the remainder of the universe.
In that case, that may remedy some of the irritating and lingering issues in cosmology, the so-called “Hubble tension.”
New analysis means that “baryon acoustic oscillations (BAOs)” from the preliminary moments of the universe, consider them as “the sound of the Big Bang,” appear to help the idea of the native void or “Hubble Bubble.”
The Hubble pressure arises from the truth that when measured utilizing completely different strategies the speed at which the universe is expanding (often known as the Hubble fixed) has completely different values. One method measures the Hubble fixed utilizing astronomical observations within the native universe, whereas the opposite provides its worth as a median throughout your complete universe.
Meaning if the native universe sits in a low-density “Hubble bubble,” it might be increasing sooner than the higher-density wider cosmos, explaining why observations give a bigger Hubble fixed worth and sooner enlargement than slower theoretical averages.
“A possible answer to this inconsistency is that our galaxy is near the middle of a giant, native void,” analysis creator Indranil Banik of the College of Portsmouth said in a statement. “It might trigger matter to be pulled by gravity in the direction of the upper density exterior of the void, resulting in the void turning into emptier with time.
“Because the void is emptying out, the speed of objects away from us could be bigger than if the void weren’t there. This, subsequently, provides the looks of a sooner native enlargement charge.”
Hubble pressure: A ‘native downside’?
There are two methods to calculate the Hubble pressure.
For one, scientists observe a “cosmic fossil” known as the cosmic microwave background (CMB). The primary gentle that was free to journey the universe, the CMB, is a area of radiation that just about evenly and uniformly fills your complete cosmos.
Scientists can observe the CMB and calculate its evolution utilizing the Lambda Cold Dark Matter model (LCDM), the usual mannequin of cosmology, as a template. From this, they derive the current-day worth for the Hubble fixed throughout the universe as some time, not simply regionally.
Alternatively, astronomers use observations of type Ia supernovas or variable stars, two examples of objects that astronomers name “standard candles,” to measure distances to their host galaxies. How briskly these galaxies are receding is revealed by the change within the wavelengths of sunshine from these our bodies, or the “redshift.” The larger the redshift, the sooner a galaxy strikes away from Earth. The Hubble fixed may be calculated from this.
The issue is that this remark methodology of the native universe provides a Hubble Fixed worth that’s larger than the theoretical worth obtained with the Lambda CDM, which considers the universe as an entire. Therefore the Hubble pressure.
Banik thinks that this discrepancy is a neighborhood downside.
“The Hubble pressure is basically a neighborhood phenomenon, with little proof that the enlargement charge disagrees with expectations in the usual cosmology additional again in time,” Banik stated. “So, a neighborhood answer like a neighborhood void is a promising solution to go about fixing the issue.”
For this native void concept to unravel the Hubble pressure, Earth and the solar system must sit roughly centrally inside the low-density Hubble bubble. The Hubble bubble must be round 2 billion light-years extensive, with a density round 20% decrease than the universe’s common matter density.
Certainly, counting the number of galaxies in the local universe does appear to disclose a decrease density than neighboring elements of the cosmos.
Nevertheless, a significant stumbling block to this idea is the truth that the existence of such an unlimited void does not match nicely with the LCDM, which suggests matter needs to be evenly unfold in all instructions, or “isotropically and homogenously” distributed by way of the universe.
New knowledge obtained by Banik exhibits that the sound of the Massive Bang, often known as Baryon Acoustic Oscillations or BAOs, really help the idea of a neighborhood void opposite to the LCDM.
“These sound waves traveled for less than a short time earlier than turning into frozen in place as soon as the universe cooled sufficient for impartial atoms to kind,” Banik defined. “They act as an ordinary ruler, whose angular dimension we are able to use to chart the cosmic enlargement historical past.”
Banik argues {that a} native void barely distorts the relation between the BAO angular scale and the redshift. It is because velocities induced by a neighborhood void and its gravitational impact barely increase the redshift along with that attributable to cosmic enlargement.
“By contemplating all accessible BAO measurements during the last 20 years, we confirmed {that a} void mannequin is about 100 million occasions extra probably than a void-free mannequin with parameters designed to suit the CMB observations taken by the Planck satellite, the so-called homogeneous Planck cosmology,” Banik added.
The subsequent step for Banik and colleagues will likely be to match their void mannequin to different fashions to attempt to reconstruct the universe’s enlargement historical past.
This might contain the usage of “cosmic chronometers,” large evolving cosmic objects like galaxies that may be aged to find out how the speed of enlargement of the universe has modified over time. With galaxies, this may be finished by observing stellar populations and seeing what sort of stars they possess, with an absence of shorter-lived massive stars indicating a extra superior age.
This age is then in contrast with the redshift the galaxy’s gentle has undergone on account of the enlargement of the universe because it traveled to us, revealing the expansion history of the universe over cosmic time.
Maybe this manner, the headache of Hubble pressure may be relieved completely.
The group’s analysis was introduced by Banik on Monday (July 7) on the Royal Astronomical Society National Astronomy Meeting (NAM) 2025 at Durham College within the UK.