Not one, however two exploding stars are presently seen to the bare eye within the southern night time sky, a cosmic coincidence that is “exceedingly uncommon” and will quickly vanish from view completely.
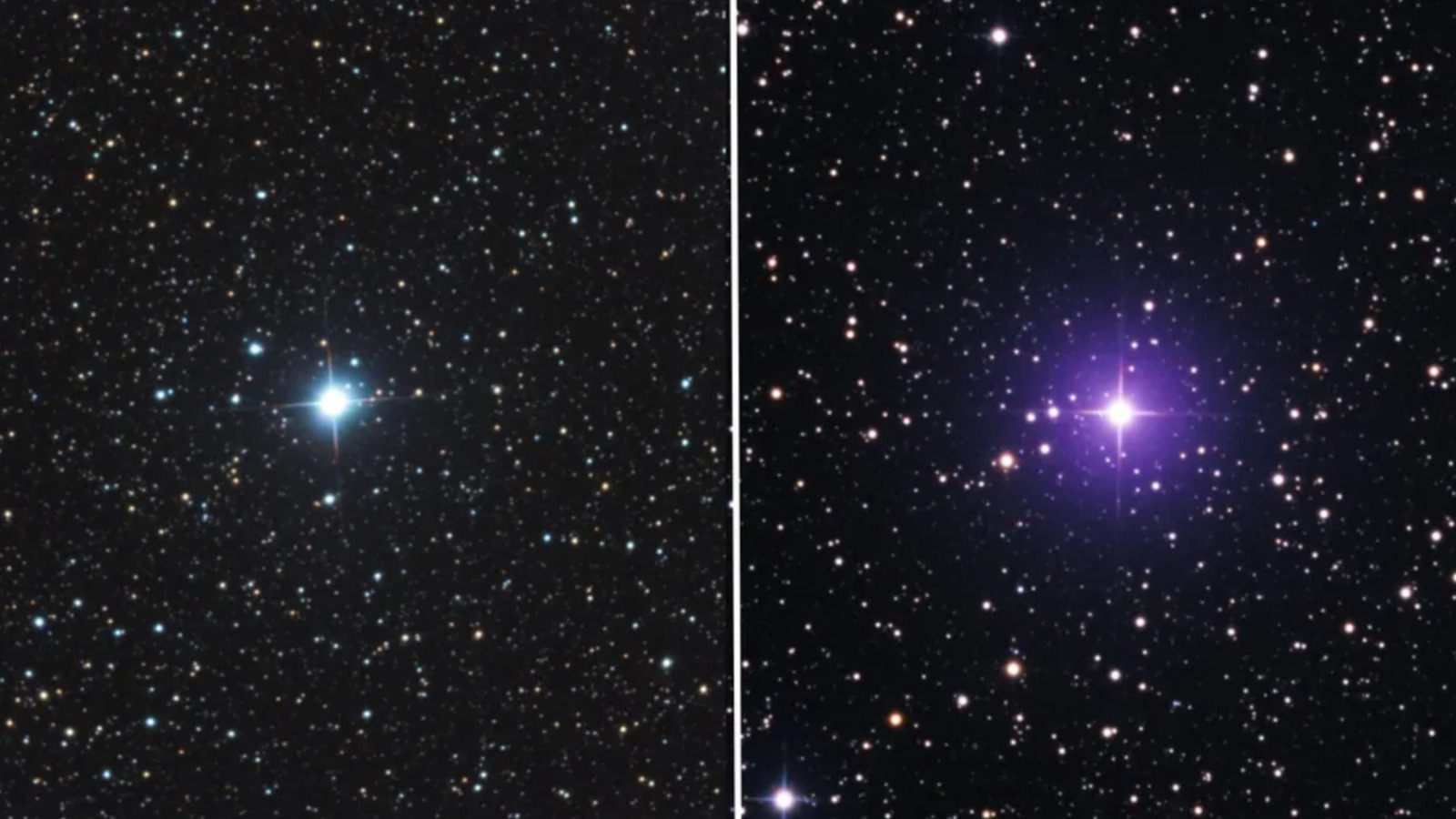
On June 12, the All-Sky Automated Survey for Supernovae (ASAS-SN), led by the Ohio State College, detected a dramatic surge within the brightness of an in any other case unremarkable star embedded within the constellation Lupus. Subsequent observations revealed a robust nova explosion — now designated V462 Lupi — to be the reason for the radiation outburst. The star shortly brightened from its beforehand dim magnitude of +22 to a peak brightness of round +5.5, rendering it seen to the bare eye.
Keep in mind, magnitude is the system utilized by astronomers to trace the brightness of an object within the night time sky. The decrease the magnitude, the brighter the thing! The human eye is able to detecting stars with a magnitude of round +6.5 or higher in darkish sky areas.
Lower than two weeks later, on June 25, stories started to flow into of a second nova blossoming within the southern night sky, this time within the constellation Vela. This nova — later designated V572 Velorum — shortly jumped to an analogous peak of +5.5, making it seem as if two new stars had abruptly burst to life within the skies south of the equator.
A nuclear explosion on the floor of a star
“Each seem like a part of binary star systems composed of a white dwarf and a companion star,” veteran science communicator and meteorologist Joe Rao advised House.com in an e-mail. “In every case, the objects that we’re capable of see visually, are seemingly being brought on by a thermonuclear explosion on the floor of the white dwarf star.”
These sorts of explosions are known as novas. In contrast to,their extra violent cousins, supernovas, these occasions do not destroy the star. As an alternative, they happen on account of a vampyric course of through which the gravitational affect of a white dwarf strips materials from a close-by companion star, including it to its personal mass. This ‘feeding’ continues till the mass of stolen stellar materials deposited on the floor of the white dwarf is heated to a vital threshold, after which a cataclysmic thermonuclear explosion is inevitable.
The ensuing outpouring of radiation results in a dramatic enhance in a star’s obvious brightness from our perspective on Earth, often making it seem as if a brand new stellar physique has burst to life within the night time sky.
“To have two naked-eye novae shining within the sky on the identical time is an exceedingly uncommon occasion”
“To have two naked-eye novae shining within the sky on the identical time is an exceedingly uncommon occasion,” stated Rao. “In checking my copy of Norton’s Star Atlas, which lists vibrant novae relationship again to the sixteenth century, I can solely discover one different case of two novae erupting so shut collectively: V368 Aquilae on September 25, 1936 and V630 Sagittarii simply eight days later.”
Rao — who serves as an teacher and visitor lecturer at New York’s Hayden Planetarium — went on to notice that the 1936 novas had pale swiftly after reaching their peaks and sure would not have been seen concurrently. Astronomer Stephen James O’Meara additionally found a 2018 prevalence through which two novas peaked and have become seen to the unaided eye on the identical day, in keeping with stargazing website Earthsky.org.
The place to seek out the novas within the southern sky
“Usually talking, most novae fade from view after just a few weeks, though some might fade a lot sooner (as was the case with the aforementioned novae in 1936) and typically the fade-down might take longer,” stated Rao. “Within the case of V572 Velorum, it apparently displays each lengthy (over 13 days) and quick (3-4 days) outbursts.”
It might nonetheless be attainable to identify the traditional mild from each novas from a darkish sky location for observers within the southern hemisphere. In the meantime, these within the southern U.S. may but glimpse V462 Lupi peeking above the horizon — maybe with the help of a pair of 10X50 binoculars.
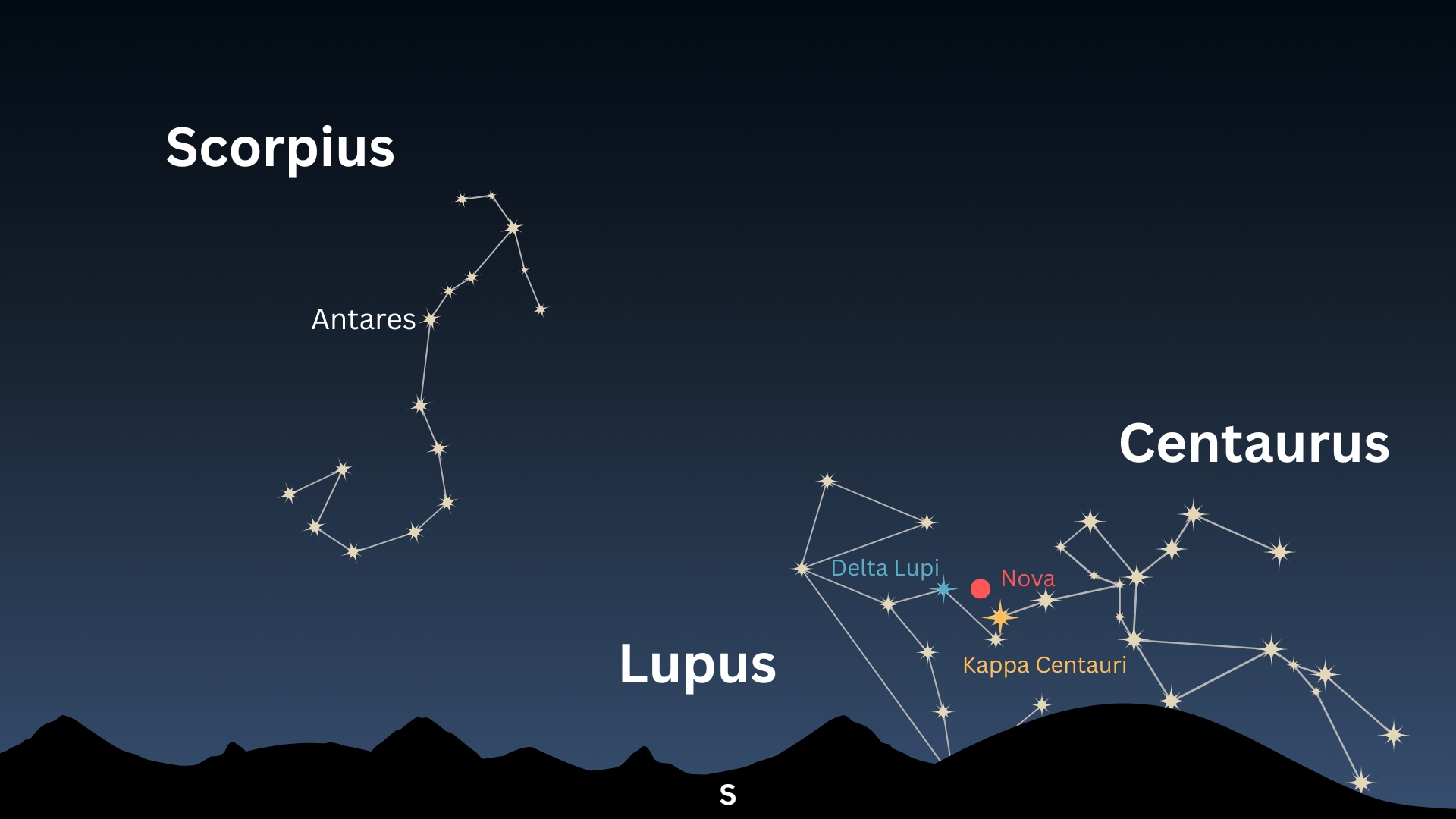
The patch of sky containing V462 Lupi is situated within the constellation Lupus, near the intense stars Delta Lupi and Kappa Centauri, from the neighboring constellation Centaurus. Lupus will likely be highest within the sky for these within the southern hemisphere, although these within the southernmost states of the U.S. might spot the constellation — and the positioning of the nova — near the southern horizon at sundown in early July.
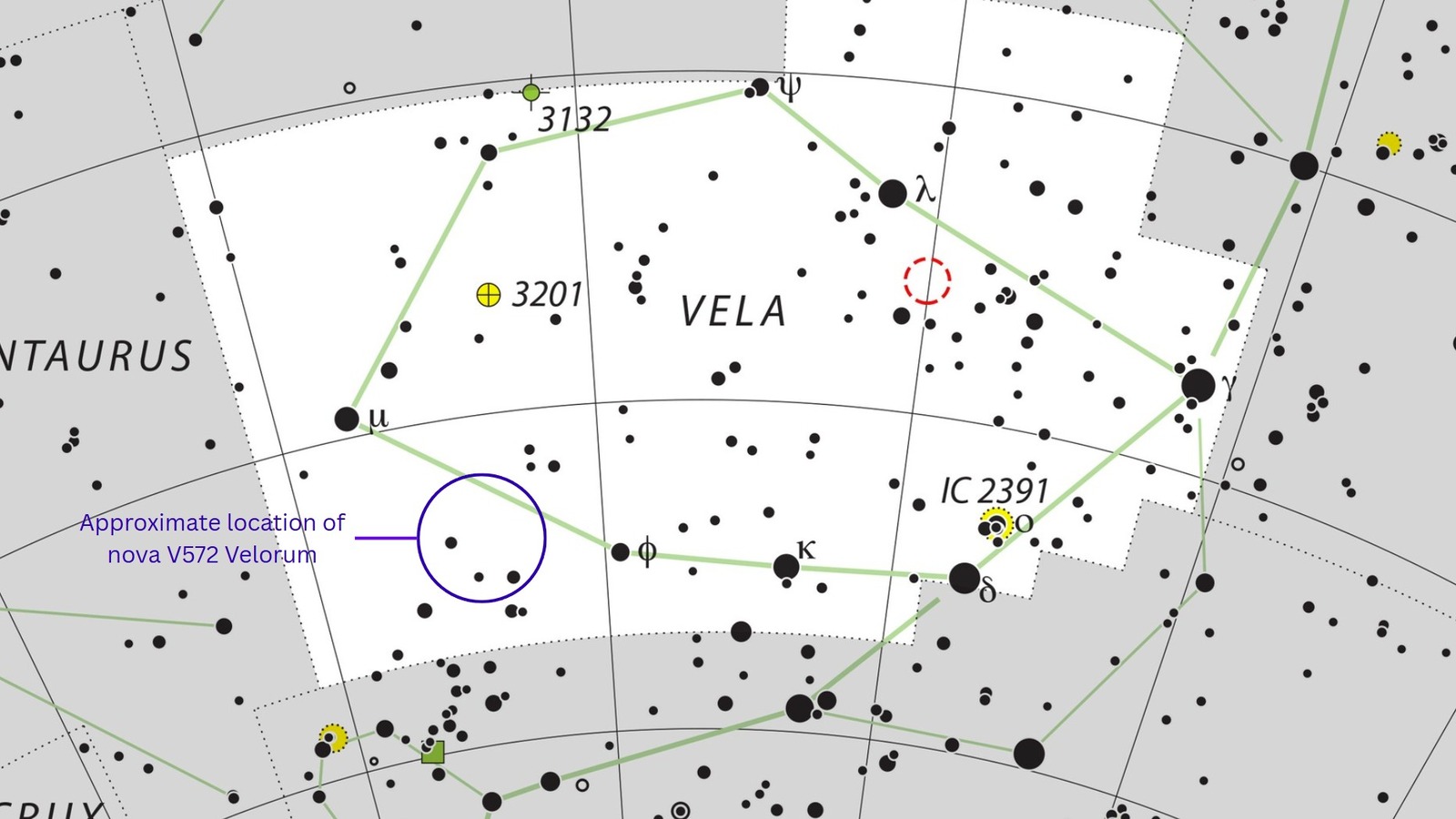
V572 Velorum in the meantime, might be discovered within the southern constellation Vela and isn’t simply seen from the continental United States. Viewers within the southern hemisphere will discover the area of sky containing the nova near the intense stars Mu Velorum and Phi Velorum.
For those who do handle to catch even a fleeting glimpse of both V572 Velorum, or V462 Lupi, you’ll have witnessed first hand one of the crucial spectacularly violent explosions that the universe has to supply. Not dangerous for one night’s stargazing.
Editor’s Notice: For those who seize a picture of a nova and need to share it with House.com’s readers, then please ship your picture(s), feedback, and your title and site to spacephotos@house.com.