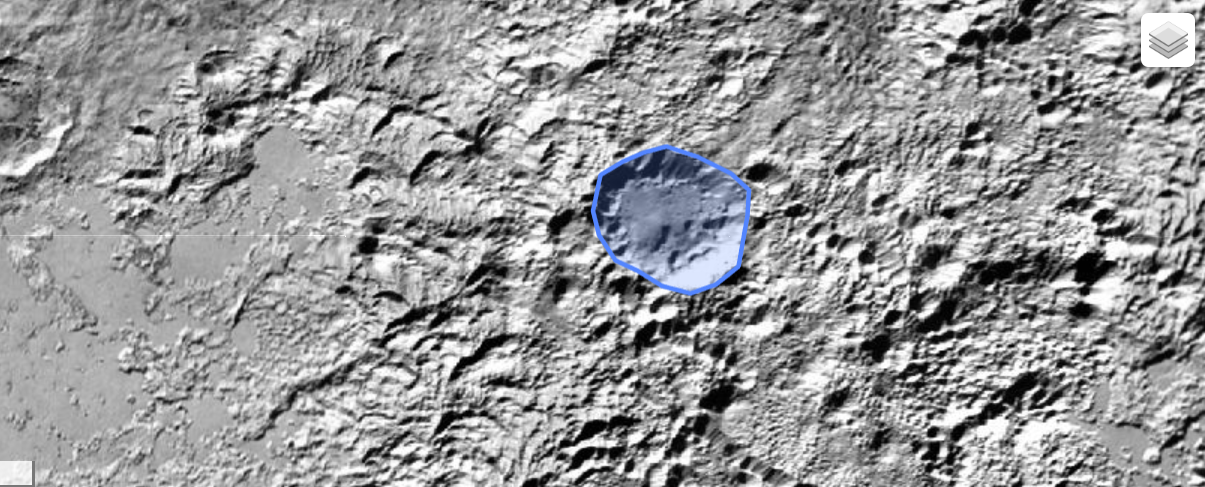
A landmark on Pluto that was beforehand designated as an impression crater may very well be the caldera of a supervolcano that has exploded up to now few million years, new analysis suggests.
When NASA’s New Horizons mission flew by Pluto in 2015, it revealed a geologically rich world, fairly than the chilly, darkish panorama many had anticipated. Virtually instantly, researchers recognized two options, known as Wright Mons and Piccard Mons, that have been strongly suspected to be icy volcanoes, and additional examine confirmed their id.
However not each cryovolcano was straightforward to identify. The suspected supervolcano, Kiladze, was initially categorised as an impression crater. Nonetheless, now scientists suspect it is one thing else.
“We evaluated the potential of the despair as a cryovolcanic caldera versus having an impression crater origin,” stated Al Emran, a planetary scientist on the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. Emran offered his crew’s ends in July on the Progress in Understanding the Pluto System: 10 Years After Flyby conference in Laurel, Maryland.
“We predict it is extra like Yellowstone Caldera in Wyoming,” Emran stated. No less than two of Yellowstone’s eruptions, thousands and thousands of years in the past, reached supervolcano standing.
Impression crater or caldera?
Kiladze stays listed as a crater. However the wealthy provide of water ice surrounding the bowl-shaped function sparked Emran’s curiosity, and he questioned if it may be a cryovolcano as an alternative.
At first look, the elongated oval bears a robust similarity to an impression crater. It is massive, with a mean diameter of two.5 miles (4 kilometers). Its partitions are irregularly formed, and the advanced options it might require may simply have been eroded by Pluto’s energetic floor processes.
The panorama itself is marked by pits and different geological options, lots of which have collapsed. If an incoming impactor broke via the floor and uncovered veins of frozen lava beneath, it may have created the explosive distribution of water ice seen on the floor.
However when Emran dug into the topography maps of Pluto created by the New Horizons crew, he realized there was an issue: The crater was too deep. Throughout the photo voltaic system, crater depth scales with crater diameter in a predictable method, and the identical regulation appeared to carry true for different craters on Pluto — however for not Kiladze.
At greatest, estimates put an impression crater of its dimension at 1.7 miles (2.74 km) large. However with the exercise flowing throughout Pluto, materials would have been extra more likely to fill within the crater over time, making it even shallower. Haze particles would have piled up, and melting or slumping ices would have fallen inward.
Nonetheless, Kiladze is not shallower than projected; it is deeper. Elements of the basin attain 2.5 deep, and the complete website averages practically 2 miles (3 km) in depth.
For these causes, Emran and his colleagues suspect that Kiladze is a caldera, a large despair created by the eruption and subsequent collapse of a volcano. Magma — or cryomagma — spewing from the floor quickly over a brief time period can weaken the supporting materials, inflicting it to break down inward on itself.
Regardless of the supervolcano’s collapse, the eruptive energy of Kiladze would have been spectacular. Emran and his colleagues calculated that the explosion may have ejected as a lot as 240 cubic miles (1,000 cubic kilometers) of icy cryomagma throughout the encompassing area, reaching the definition of a supervolcano. Though Yellowstone has erupted greater than 80 instances over its lifetime of greater than 2 million years, solely two explosions have been categorised as supervolcanic.
Kiladze could have blasted out its cryomagma in a single explosive occasion, or it might have unfold its eruptions over time. Both method, its most up-to-date occasion spewed water ice no less than 60 miles (100 km). Emran suspects that estimate is low, nevertheless, as extra water ice is probably going seen at resolutions smaller than New Horizons may attain.
“A number of cataclysmic explosive eruptions that resulted within the excavation and collapse of what’s seen because the Kiladze caldera could be anticipated to scatter the water-ice cryomagma extensively for a thousand or extra kilometers, leaving exposures too small to be seen within the information at hand,” the authors wrote in a paper not too long ago printed in The Planetary Science Journal.
Clues within the ice
Kiladze sits simply north of Sputnik Planetia, the icy coronary heart to Pluto. Though a lot of the dwarf planet’s floor is roofed with a wide range of ices, little or no of the floor matches what you may discover in your freezer at dwelling. Temperatures on Pluto are so chilly that water ice serves because the bedrock for the dwarf planet, whereas different ices pile on high.
However within the neighborhood surrounding Kiladze, water ice stretches throughout the floor. The ice has traces of an unidentified ammoniated compound. “It is troublesome to find out the precise composition,” Emran stated. In reality, that exact signature of ammonia is just not seen wherever else on Pluto.
Ammonia could also be what permits the frigid ice to circulate. Its addition lowers the freezing level of water, permitting it to stay liquid for longer durations. Beneath the floor, pockets of water and ammonia may have prevented freezing as Pluto’s bedrock solidified. Finally, tectonic strain may have pushed the icy magma to the floor, spewing it throughout the panorama round Kiladze, Emran defined.
The mysterious traces of ammonia may additionally assist up to now the cryovolcano. Pure ammonia is shortly obliterated by the solar wind, ultraviolet particles and cosmic rays. Its faint presence means that the internet eruption occurred pretty not too long ago in Pluto’s historical past, Emran stated.
Pluto’s haze might help to nail down geological exercise. The sunshine shroud covers the dwarf planet — a results of methane and different gases leaping from strong to fuel. Because the particles develop, they finally fall again to the floor and unfold all around the dwarf planet. Grounded haze particles would cowl the water ice like a blanket, obscuring indicators of the cryolava, Emran defined. If such a layer had shaped, New Horizons would have seen nitrogen-rich ice as an alternative of indicators of water-rich volcanism.
Burying the water ice requires no less than 0.4 inches (10 millimeters) of haze particles falling to Pluto. That course of takes no less than 3 million years, Emran stated. That would imply Pluto is not as frozen as beforehand thought.
“If Kiladze erupted as not too long ago as 3 million years in the past, it might certainly counsel that Pluto’s inside should still retain some residual heat at this time,” Emran stated. “This aligns with the concept cryovolcanism on Pluto could possibly be ongoing or episodic.”