13 years into its mission, NASA’s Curiosity rover continues to be uncovering Martian mysteries — and studying to do extra with much less.
Since touchdown in Gale Crater in 2012, Curiosity has traveled greater than 22 miles (35 kilometers), learning rock layers, analyzing soil and revealing Mars’ historic previous, together with indicators that the planet as soon as harbored liquid water, a thicker atmosphere and situations that may have supported microbial life. And regardless of the toll of time, together with worn wheels and mechanical glitches, engineers have stored the rover rolling with inventive workarounds, distant fixes and adaptive driving methods.
Now, due to current software program upgrades, the rover has gained new autonomy that permits it to multitask and put itself to sleep early when it finishes its each day duties, NASA mentioned in a statement. This new skill helps preserve vitality from its growing older nuclear energy supply and lengthen its scientific lifespan, the assertion learn.
“We had been extra like cautious dad and mom earlier within the mission,” mentioned Reidar Larsen, a flight methods engineer at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California, who led the group behind the brand new capabilities. “It is as if our teenage rover is maturing, and we’re trusting it to tackle extra accountability.”
Curiosity, which is the dimensions of a small SUV, is powered by a multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG), which converts warmth from the pure decay of plutonium into electricity to recharge the rover’s batteries. However because the plutonium decays, the system step by step produces much less vitality, which means it takes longer to recharge the batteries and leaves much less energy for science every day.
To take advantage of the diminishing vitality provide, engineers have been working to spice up the rover’s effectivity by combining beforehand standalone duties like driving, taking pictures and transmitting knowledge, in keeping with the NASA assertion.
By consolidating these actions, engineers have been capable of shorten every day’s operational plan, decreasing the period of time heaters and devices want to remain powered on, saving priceless vitality within the course of, the assertion learn.
And as a substitute of idling whereas ready for brand spanking new instructions, Curiosity can now put itself to sleep as quickly because it finishes the day’s work. These small changes — even trimming simply 10 or 20 minutes per day — can add up over time and assist protect energy and lengthen the rover’s mission, the company wrote within the assertion.
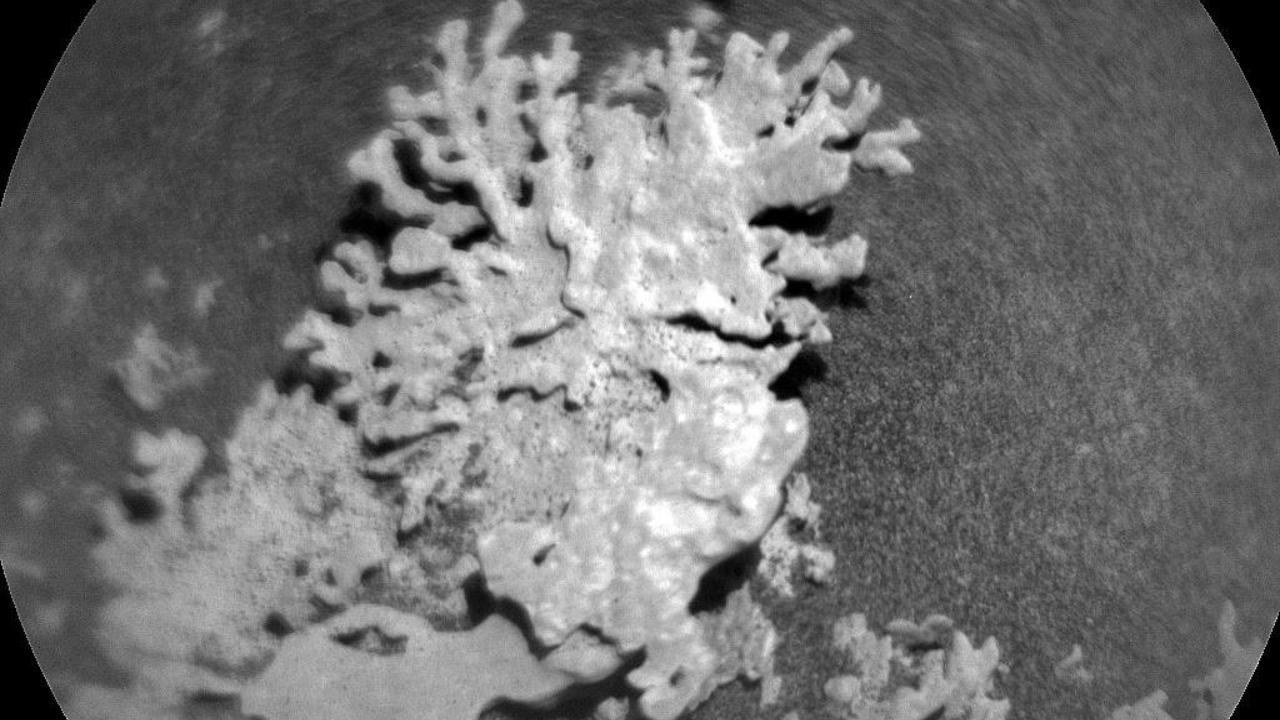
These new energy-saving habits come because the rover has noticed an attention grabbing rock formation that resembles a bit of coral. Captured on July 24, 2025, the rock, nicknamed “Paposo,” is about two inches (5 centimeters) large and was photographed utilizing a digital camera perched on the finish of the rover’s robotic arm, in keeping with the assertion.
Paposo seemingly shaped billions of years in the past throughout a time when Mars was a lot wetter than it’s as we speak, the assertion says. Mineral-rich water seemingly seeped into cracks within the rock, forsaking hardened deposits. Over time, highly effective winds would have sculpted the uncovered materials into the fragile, branching form seen by the rover.
Curiosity is presently exploring a area wealthy in so-called “boxwork formations,” a community of ridges that seemingly shaped underground by means of historic water exercise. These options crisscross the decrease slopes of Mount Sharp, the three-mile-high (five-kilometer-high) mountain above the ground of Gale Crater that the rover has been ascending for years.
All in all, Curiosity stays in good well being, NASA says, bolstered by sensible engineering, up to date algorithms, and now, a bit extra relaxation.
“Collectively, these measures are doing their job to maintain Curiosity as busy as ever,” the company’s assertion says