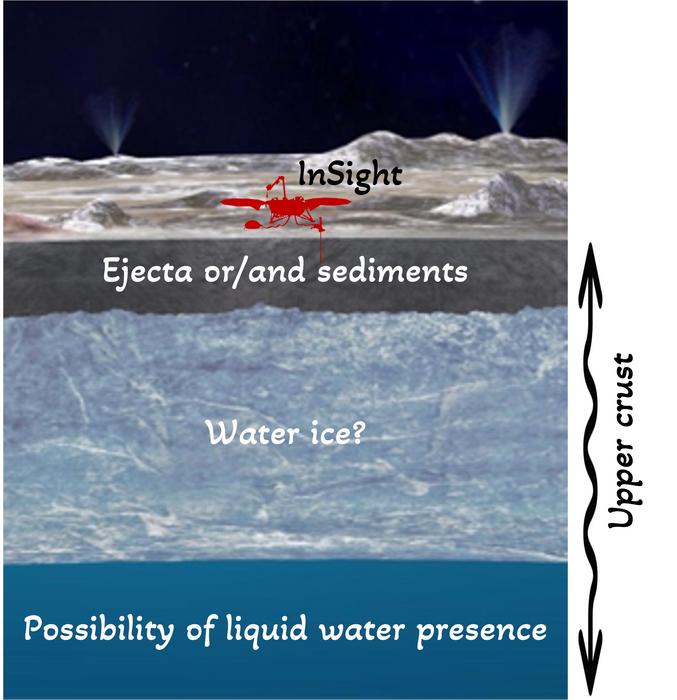
Scientists have discovered seismic clues that counsel liquid water could also be hiding beneath Mars’ floor.
By listening to the echoes of “marsquakes” — seismic waves rippling by way of Mars‘ crust — researchers uncovered indicators of water lingering on the base of the planet’s higher crust, which sits between 3.4 and 5 miles (5.4 and eight kilometers) under the floor.
“Inside our solar system, Mars has constantly been on the forefront of the seek for extraterrestrial life,” stated Weijia Solar, a professor on the Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese language Academy of Sciences and one of many research’s authors, to House. “The presence of liquid water is considered one of the vital crucial elements on this endeavor.”
Liquid water was thought to as soon as stream freely throughout Mars in the course of the planet’s Noachian and Hesperian durations — an period stretching from the planet’s formation as much as about 3 billion years in the past. Nevertheless, as Mars entered the Amazonian interval, its local weather dramatically shifted. Floor water disappeared, forsaking the chilly, dry panorama we see at the moment.
“Whereas the presence of flowing water on Mars is now indeniable, the quantity and mechanisms of its disappearance stay topics of energetic debate,” stated Solar.
One principle suggests Mars misplaced its water to area as photo voltaic wind stripped it from the environment — a course of supported by ratios of isotopes on the Purple Planet, or distinct species of chemical parts, seen at the moment. One other proposes that the water did not vanish, however reasonably sank into the crust. This may counsel pockets of water in deep underground aquifers. Whereas some fashions predict liquid water might survive within the center crust, its extent stays unsure as a consequence of an absence of detailed structural knowledge from these depths.
NASA and different area businesses have despatched rovers and orbiters geared up with ground-penetrating radar to discover beneath Mars’ floor — however these instruments can solely see a number of miles deep. That is as a result of electromagnetic indicators rapidly fade as you go deeper into the crust.
However Solar and his workforce took a unique method. As an alternative of radar, they tapped into knowledge of seismic waves generated by two large meteorite impacts (S1000a and S1094b) and the biggest recorded marsquake (S1222a). “Whereas earlier computational research have steered the potential presence of liquid water on Mars, these predictions lacked observational assist that seismology provides,” he stated.
By analyzing how these waves traveled by way of the crust, they have been in a position to map its fantastic construction — and seek for anomalies that may trace at liquid water. “We used a way referred to as ‘receiver capabilities,’ which signify the signatures of seismic waves as they replicate and reverberate between crustal layers, analogous to echoes mapping a cave,” Hrvoje Tkalčić, a professor at The Australian Nationwide College and co-author of the research, advised House.com. “These signatures allow the exact identification of the thicknesses of layers and the depth to the boundaries the place rock properties change.”
“In contrast to conventional receiver perform strategies, we introduce the idea of true-amplitude imaging, a way tailored from the oil exploration subject, which considerably improves decision and permits the detection of a lot smaller constructions,” Solar stated. “The true-amplitude receiver perform acts as a magnifying glass, enhancing the readability of subsurface options.”
The workforce’s evaluation revealed an uncommon zone deep underground at about 3 to five miles (5 to eight kilometers) the place seismic waves slowed down. Initially, this was regarded as the results of a fractured sedimentary layer of rock, the place diminished stiffness and elevated compliance make the rock much less in a position to transmit a wave’s power. Nevertheless, primarily based on its place throughout the crust, it was unlikely this layer was made up of sediments.
“Generally, seismic waves propagate considerably quicker by way of dry rock than by way of water-saturated rock,” stated Solar. As an alternative, the workforce suggests this “low velocity” layer might truly be crammed with liquid water as a result of rocks on this space, referred to as altered basalts, have excessive porosity, which could enable them to carry water.
“By means of a complete evaluation, we inferred that the low-velocity layer might be attributed to the presence of liquid water, the place temperatures exceed the freezing level throughout the specified depth vary,” Solar stated.
Primarily based on their knowledge, they estimated the existence of between 569 and 853 yards (520–780 meters) of World Equal Layer (GEL) — a metric used to quantify the quantity of water when distributed uniformly throughout all the floor of a planet or moon. This quantity roughly coincides with the between 776 and 1,006 (710 and 920 meter) GEL, that can not be accounted for with Mars’ present-day water stock.
“The presence of subsurface water on Mars holds vital implications for future human missions and the potential for extraterrestrial life,” stated Tkalčić. “Nevertheless, drilling or extracting water from deep underground would necessitate superior expertise and substantial power sources.”
Whereas this research gives crucial insights into the Martian water cycle and the evolution of its setting, the researchers emphasize that their estimate is predicated solely on knowledge gathered from a neighborhood profile beneath the InSight lander, situated within the Elysium Planitia area, about 4.5 levels north of the Martian equator.
This might imply the findings are particular to this specific space and will not totally signify the planet’s complete floor. “This limitation may be addressed by future missions geared up with seismometers on Mars,” concluded Tkalčić.
The research was published on April 25 within the journal Nationwide Science Evaluate.