It was weirdly emotional on Monday (June 23) as a number of grainy white specks streaked throughout my laptop display whereas ambient rhythms buzzed within the background. These specks had been a part of a movie that performed through the Vera C. Rubin Observatory’s extremely anticipated first picture launch convention — and so they every represented an asteroid that had simply been found. It felt like witnessing one thing massively profound, and there are two the reason why.
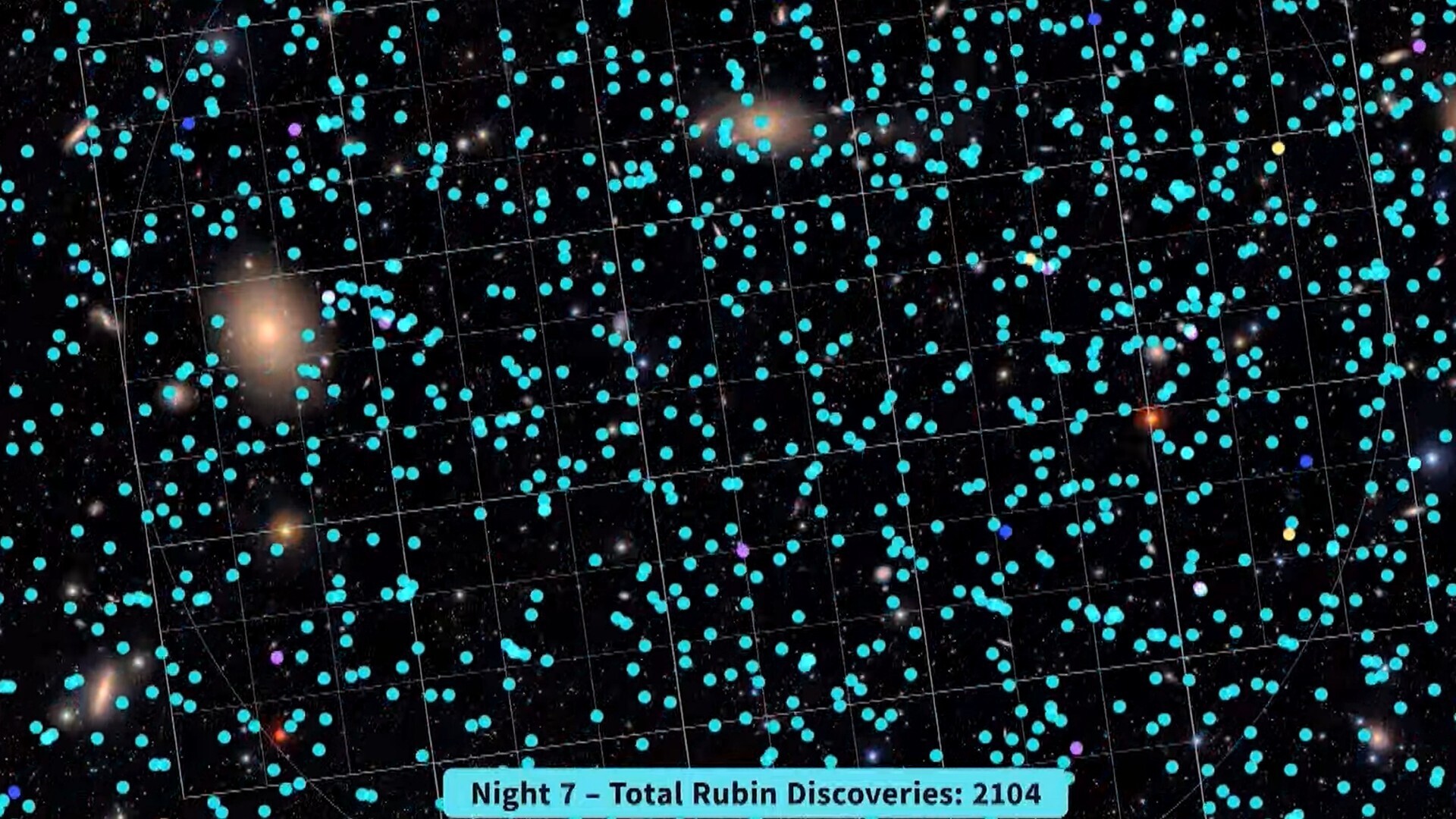
Initially, to place it merely, with just some nights of information, the Rubin Observatory workforce was in a position to determine 2,104 never-before-seen asteroids in our photo voltaic system — seven of that are categorized as near-Earth objects. (No, none are anticipated to strike our planet. Don’t be concerned). For context, there are roughly one million recognized asteroids in our cosmic neighborhood; over the subsequent few years, Rubin might very nicely hike that determine as much as 5 million.
“That is 5 occasions greater than all of the astronomers on the earth found over the last 200 years because the discovery of the primary asteroid,” Željko Ivezić, Deputy Director of Rubin’s Legacy Survey of Area and Time, stated through the convention. “We will outdo two centuries of effort in simply a few years.”
That is astonishing in itself — speak about an exemplary first impression — however there’s nonetheless that second factor that makes Rubin’s new asteroid knowledge unimaginable.
They are often formatted as motion pictures.
Welcome to Hollywood, asteroids
For some context about Rubin, this observatory is our sensible new ground-based eye on the universe, and is situated on the El Peñón peak of Cerro Pachón in Chile. It has the power to picture big swaths of the sky utilizing the world’s largest digital digicam — and after I say big, I imply big.
One in every of its first offered photographs, as an illustration, incorporates a bunch of glowing, hazy galaxies of all sizes and shapes. It is troublesome to not daydream when a few beautiful lavender spirals that signify realms similar to our complete Milky Method.
However what you see beneath on this picture is just 2% of the total Rubin view:
The plan is for Rubin to seize such large, high-resolution photographs of the southern sky as soon as each three nights for no less than the subsequent 10 years. You may due to this fact take into account it to be a super-fast, super-efficient and super-thorough cosmic imager. Certainly, these qualities are excellent for recognizing a number of the smallest particulars trailing via the area round our planet: asteroids.
“We make motion pictures of the night time sky to see two issues: objects that transfer and objects that change brightness,” Ivezić stated. “Objects that transfer are available two flavors. Stars in our galaxy transfer, and so they transfer slowly. A lot quicker objects are asteroids.”
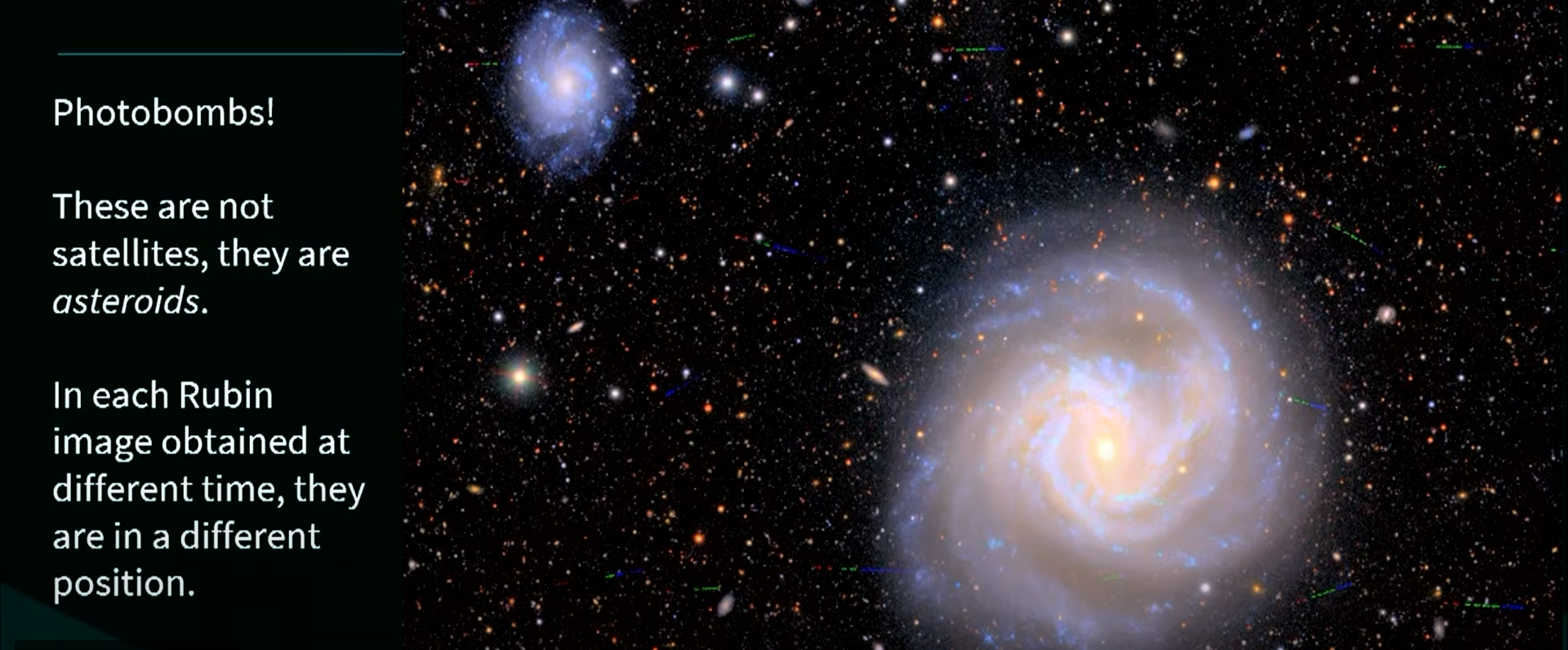
Zooming right into a tiny portion of one among Rubin’s photographs, Ivezić identified that there are literally invisible photobombers current. He was speaking concerning the asteroid streaks Rubin’s software program so kindly faraway from the principle attraction (I imply, take a look at that spiral). Nevertheless, the truth that these asteroids will be faraway from a picture means they are often exactly remoted to start with, making it doable to actually concentrate on them if you wish to — one thing that is not all the time doable with zippy, fleeting area objects.
In reality, it is tremendously troublesome to document an asteroid in any respect.
“Asteroids, they disappear after you get one image of them,” Ivezić stated, calling Rubin’s skill to picture small objects orbiting the solar “unprecedented.”
Within the Rubin picture Ivezić referred to as out to showcase the observatory’s asteroid-tracking capabilities, the asteroid streaks are seen in several colours. It is because every corresponds to 1 publicity used to create the ultimate picture. You may consider it as totally different photographs stitched collectively to create a closing view of the asteroids’ trajectories. And to take issues a step additional, in case you slap a number of of those datasets collectively, you may point out asteroid movement towards the extra static background of stars and galaxies — like a film.
This characteristic of Rubin needs to be large not solely as a result of it’d enable scientists to higher examine asteroid actions and uncover new near-Earth objects, but additionally for humanity’s efforts in planetary protection.
Over the past couple of years, scientists have actually began to query how we will shield our planet if an asteroid had been headed our method.
NASA’s wildly profitable DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Check) mission — which despatched a spacecraft on a demise mission to crash into an asteroid and see if the article’s trajectory will be modified — was arguably the feat that introduced planetary protection to the general public eye. It’d even be remiss to not point out all of the current anxiousness surrounding Asteroid 2024 YR4, which was potent sufficient to even penetrate the jokes of a random comedy present in New York Metropolis I went to across the time it was making headlines. 2024 YR4 briefly had a head-turning probability of hitting our planet earlier than that probability shot right down to nil.
There was even a hearing about asteroid security in Might, held by the U.S. Home Committee on Area, Science and Expertise, throughout which U.S. Representatives expressed their concern that asteroid protection could also be impacted by President Trump’s main science funding cuts.
All of that is to say that I think about a state-of-the-art asteroid detector could be very welcome within the scientific neighborhood proper now.
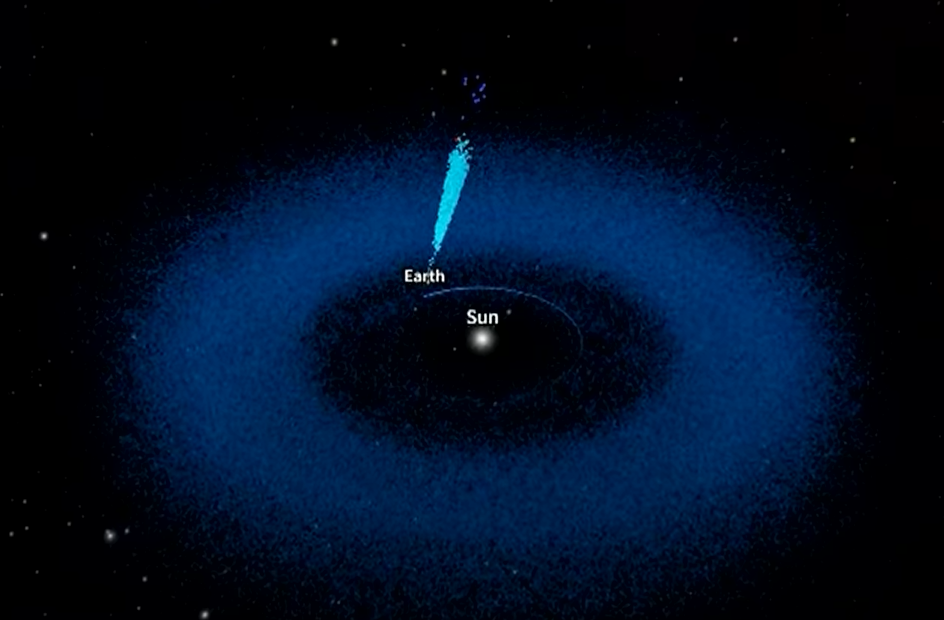
To actually illustrate the last word promise of Rubin’s asteroid adventures, Ivezić introduced up a simulation of all asteroids anticipated to orbit our solar.
“This blue donut is a simulation of all asteroids we anticipate there,” he stated. “All of those new discoveries are discovered on this one slender slice of this massive donut. In two or three years, after we begin LSST later this 12 months, we’ll sweep round and uncover the entire thousands and thousands of asteroids.”